|
(2nd April 2023)
|
|
Bananagrams is a real-time word game in which participants race to build their own crosswords. It requires comprehensive vocabulary, fast thinking and good decision making. Some times situations arise which require an either-or decision: do I scrap my partial solution and do a fresh start or not? Or you may be left with one unusable extra letter, which you can put back into the pile and pick up three random new ones. This first article of the topic describes a two-phase artificial neural network which detects and identifies the tiles from an image. The second article will describe how to generate a valid crossword from given letters.
|
|
|
(10th November 2022)
|
|
Stable Diffusion is an image generation network, which was released to the public in 2022. It is based on a diffusion process, in which the model gets a noisy image as an input and it tries to generate a noise-free image as an output. This process can be guided by describing the target image in plain English (aka txt2img), and optionally even giving it a target image (aka. img2img). This article doesn't describe how the model works and how to run it yourself, instead this is more of a tutorial on how various parameters affect the resulting image. Non-technical people can use these image generating AIs via webpages such as Artistic.wtf (my and my friend's project), Craiyon.com, Midjourney.com and others.
|
|
|
(19th July 2022)
|
|
Some people enjoy solving puzzles in the old fashioned way, but engineers would like to automate tedious tasks like that. This is a well-suited task for supervised learning, but naturally it requires training data. Gathering it from real-life puzzles would be time-consuming as well, so I opted for generating it instead. This gives a lot of control on the data, but the resulting system might not even work with real-life inputs. There are also several different styles of puzzles, but in this project each "base-piece" is a rectangle of identical size. An example 3 × 3 puzzle is shown in the thumbnail.
|
|
|
(15th January 2022)
|
|
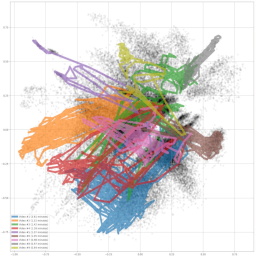
This article describes a neural network which automatically projects a large collection of video frames (or images) into 2D coordinates, based on their content and similarity. It can be used to find content such as explosions from Arnold's movies, or car scenes from Bonds. It was originally developed to organize over 6 hours of GoPro footage from Åre bike trip from the summer of 2020, and create a high-res poster which shows the beautiful and varying landscape (Figure 9).
|
|
|
(15th December 2021)
|
|
The Finnish Inverse Problems Society (FIPS) organized the Helsinki Deblur Challenge 2021 during the summer and fall of 2021. The challenge is to "deblur" (deconvolve) images of a known amount of blur, and run the resulting image through and OCR algorithm. Deblur-results are scored based on how well the pytesseract OCR algorithm is able to read the text. They also kindly provided unblurred versions of the pictures, so we can train neural networks using any supervised learning methods at hand. The network described in this article isn't officially registered to the contest, but since the evaluation dataset is also public we can run the statistics ourselves. Hyperparameter tuning got a lot more difficult once it started taking 12 - 24 hours to train the model. I might re-visit this project later, but here its status described as of December 2021. Had the current best network been submitted to the challenge, it would have ranked 7th out of the 10 (nine plus this one) participants. There is already a long list of known possible improvements at the end of this article, so stay tuned for future articles.
|
|
|
(13th June 2021)
|
|
Youtube has a quite good search functionality based on video titles, descriptions and maybe even subtitles but it doesn't go into actual video contents and provide accurate timestamps for users' searches. An youtuber "Agadmator" has a very popular channel (1.1 million subscribers, 454 million video views at the time of writing) which showcases major chess games from past and recent tournaments and online games. Here a search engine is introduced which analyzes the videos, recognizes chess pieces and builds a database of all of the positions on the board ready to be searched. It keeps track of the exact timestamps of the videos in which the queried position occurs so it is able to provide direct links to relevant videos.
|
|
|
(10th September 2014)
|
|
Nowadays there are many HTML5-based map services, but typically they don't offer any export functionality. To create a full view of the desired region, one can either zoom out (and lose map details) or take many screenshots of different locations and manually stitch them together. This project can automatically load all stored screenshots, detect the map, crop relevant regions, determine images relative offsets and generate the high-res output with zero configuration from any map service.
|
|
|
(9th August 2014)
|
|
This project's goal was to automatically and robustly estimate and compensate distortion from any receipt photos. The user is able to just snap the photo and OCR could accurately identify bought products and their prices. However this task is somewhat challenging because typically receipts tend to get crumbled and bent. Thus they won't lie nicely flat on a surface for easy analysis. This set of algorithms solves that problem and produces distortion-free thresholded images for the next OCR step.
|
|
|
(7th June 2014)
|
|
From my office window I've got an unblocked size-view to the Ring Road I (Kehä I) in Espoo, Finland. It is one of the busiest roads in Finland, having up-to 100.000 cars / day. I wanted to create a program which would receive a video feed from a webcam and would process images in real time on common hardware.
|
|
|
(15th July 2013)
|
|
As mentioned in an other article about omnidirectional cameras, my Master's Thesis' main topic was real-time interest point extraction and tracking on an omnidirectional image in a challenging forest environment. I found OpenCV's routines mostly rather slow and running in a single thread, so I ended up implementing everything myself to gain more control on the data flow and threads' dependencies. The implemented code would simultaneously use 4 threads on CPU and a few hundred on the GPU, executing interest point extraction and matching at 27 fps (37 ms/frame) for 1800 × 360 pixels (≈0.65 Mpix) panoramic image.
|
|
|
(6th July 2013)
|
|
My Masters of Science Thesis involved the usage of a so-called "omnidirectional camera". There are various ways of achieving 180° or even 360° view, with their distinct pros and cons. The general benefit of these alternative camera systems is that objects don't need to be tracked, because generally they stay withing the extremely broad Field of View (FoV) of the camera. This is also very beneficial in visual odometry tasks, because landmarks can be tracked for longer periods of time.
|
|
|
(26th June 2013)
|
|
I developed a coin recognition system which can recognize eight different groups of coins. The used set is all five coins of Singapore, but a few categories cannot be distinguished from each other without knowledge of the coin's size in relation to others.
|
|
|
(25th June 2013)
|
|
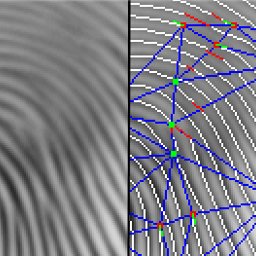
For my Bachelor of Science degree I developed a novel fingerprint matching algorithm, which ended up beating many alternative methods which were developed by research groups around the world. The used dataset the same which was used for FVC 2000 (Fingerprint Verification Competition).
|
|